Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | network solid | e. | tetrahedral angle | b. | bonding orbital | f. | VSEPR theory | c. | dipole
interaction | g. | sigma
bond | d. | bond dissociation energy |
|
|
|
1.
|
energy needed to break a single bond between two covalently bonded
atoms
|
|
|
2.
|
symmetrical bond along the axis between the two nuclei
|
|
|
3.
|
molecular orbital that can be occupied by two electrons of a covalent
bond
|
|
|
4.
|
109.5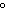
|
|
|
5.
|
shapes adjust so valence-electron pairs are as far apart as possible
|
|
|
6.
|
attraction between polar molecules
|
|
|
7.
|
crystal in which all the atoms are covalently bonded to each other
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
8.
|
Sigma bonds are formed as a result of the overlapping of which type(s) of atomic
orbital(s)?
a. | s only | c. | d only | b. | p only | d. | s and
p |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following bond types is normally the weakest?
a. | sigma bond formed by the overlap of two s orbitals | b. | sigma bond formed by
the overlap of two p orbitals | c. | sigma bond formed by the overlap of one s
and one p orbital | d. | pi bond formed by the overlap of two p
orbitals |
|
|
|
10.
|
According to VSEPR theory, molecules adjust their shapes to keep which of the
following as far apart as possible?
a. | pairs of valence electrons | c. | mobile
electrons | b. | inner shell electrons | d. | the electrons closest to the nuclei |
|
|
|
11.
|
The shape of the methane molecule is called ____.
a. | tetrahedral | c. | four-cornered | b. | square | d. | planar |
|
|
|
12.
|
What causes water molecules to have a bent shape, according to VSEPR
theory?
a. | repulsive forces between unshared pairs of electrons | b. | interaction between
the fixed orbitals of the unshared pairs of oxygen | c. | ionic attraction and
repulsion | d. | the unusual location of the free electrons |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following theories provides information concerning both molecular
shape and molecular bonding?
a. | molecular orbital theory | c. | orbital hybridization
theory | b. | VSEPR theory | d. | Bohr atomic theory |
|
|
|
14.
|
Experimental evidence suggests that the H—C—H bond angles in ethene,
C 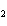 H 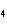 , are ____.
|
|
|
15.
|
What type of hybrid orbital exists in the methane molecule?
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the shape of a molecule with a triple bond?
a. | tetrahedral | c. | bent | b. | pyramidal | d. | linear |
|
|
|
17.
|
What type of hybridization occurs in the orbitals of a carbon atom participating
in a triple bond with another carbon atom?
|
|
|
18.
|
How many pi bonds are formed when sp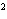 hybridization
occurs in ethene, C 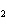 H 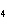 ?
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following atoms acquires the most negative charge in a covalent
bond with hydrogen?
|
|
|
20.
|
A bond formed between a silicon atom and an oxygen atom is likely to be
____.
a. | ionic | c. | polar covalent | b. | coordinate covalent | d. | nonpolar
covalent |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following covalent bonds is the most polar?
|
|
|
22.
|
When placed between oppositely charged metal plates, the region of a water
molecule attracted to the negative plate is the ____.
a. | hydrogen region of the molecule | c. | H—O—H plane of the
molecule | b. | geometric center of the molecule | d. | oxygen region of the
molecule |
|
|
|
23.
|
What is thought to cause the dispersion forces?
a. | attraction between ions | c. | sharing of electron
pairs | b. | motion of electrons | d. | differences in electronegativity |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the forces of molecular attraction is the weakest?
a. | dipole interaction | c. | hydrogen bond | b. | dispersion | d. | single covalent
bond |
|
|
|
25.
|
What causes dipole interactions?
a. | sharing of electron pairs | b. | attraction between polar
molecules | c. | bonding of a covalently bonded hydrogen to an unshared electron
pair | d. | attraction between ions |
|
|
|
26.
|
What are the weakest attractions between molecules?
a. | ionic forces | c. | covalent forces | b. | Van der Waals forces | d. | hydrogen forces |
|
|
|
27.
|
What causes hydrogen bonding?
a. | attraction between ions | b. | motion of electrons | c. | sharing of electron
pairs | d. | bonding of a covalently bonded hydrogen atom with an unshared electron
pair |
|
|
|
28.
|
Why is hydrogen bonding only possible with hydrogen?
a. | Hydrogen’s nucleus is electron deficient when it bonds with an electronegative
atom. | b. | Hydrogen is the only atom that is the same size as an oxygen
atom. | c. | Hydrogen is the most electronegative element. | d. | Hydrogen tends to
form covalent bonds. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which type of solid has the highest melting point?
a. | ionic solid | c. | metal | b. | network solid | d. | nonmetallic
solid |
|
|
|
30.
|
What is required in order to melt a network solid?
a. | breaking Van der Waals bonds | c. | breaking hydrogen
bonds | b. | breaking ionic bonds | d. | breaking covalent bonds |
|