Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | electronegativity | f. | periodic law | b. | ionization energy | g. | cation | c. | atomic
radius | h. | period | d. | metal | i. | group | e. | transition
metal | j. | electrons |
|
|
|
1.
|
one-half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms when the atoms are
joined
|
|
|
2.
|
type of ion formed by Group 2A elements
|
|
|
3.
|
subatomic particles that are transferred to form positive and negative
ions
|
|
|
4.
|
ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound
|
|
|
5.
|
energy required to remove an electron from an atom
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
6.
|
What element in the second period has the largest atomic radius?
a. | carbon | c. | potassium | b. | lithium | d. | neon |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following factors contributes to the increase in atomic size within
a group in the periodic table as the atomic number increases?
a. | more shielding of the electrons by the highest occupied energy
level | b. | an increase in size of the nucleus | c. | an increase in number of
protons | d. | fewer electrons in the highest occupied energy level |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following elements has the smallest atomic radius?
a. | sulfur | c. | selenium | b. | chlorine | d. | bromine |
|
|
|
9.
|
What is the charge of a cation?
a. | a positive charge | b. | no charge | c. | a negative
charge | d. | The charge depends on the size of the nucleus. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following statements is true about ions?
a. | Cations form when an atom gains electrons. | b. | Cations form when an
atom loses electrons. | c. | Anions form when an atom gains
protons. | d. | Anions form when an atom loses protons. |
|
|
|
11.
|
The metals in Groups 1A, 2A, and 3A ____.
a. | gain electrons when they form ions | c. | all have ions with a 1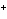 charge
charge | b. | all form ions with a negative charge | d. | lose electrons when they form
ions |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following statements is NOT true about ions?
a. | Cations are positively charged ions. | b. | Anions are common among
nonmetals. | c. | Charges for ions are written as numbers followed by a plus or minus
sign. | d. | When a cation forms, more electrons are transferred to
it. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Why is the second ionization energy greater than the first ionization
energy?
a. | It is more difficult to remove a second electron from an atom. | b. | The size of atoms
increases down a group. | c. | The size of anions decreases across a
period. | d. | The nuclear attraction from protons in the nucleus
decreases. |
|
|
|
14.
|
In which of the following sets are the charges given correctly for all the
ions?
|
|
|
15.
|
In which of the following groups of ions are the charges all shown
correctly?
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the element with the lowest electronegativity value?
a. | cesium | c. | calcium | b. | helium | d. | fluorine |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the element with the highest electronegativity value?
a. | cesium | c. | calcium | b. | helium | d. | fluorine |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following elements has the smallest ionic radius?
|
|
|
19.
|
What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous
state called?
a. | nuclear energy | c. | shielding energy | b. | ionization energy | d. | electronegative
energy |
|
|
|
20.
|
For Group 2A metals, which electron is the most difficult to remove?
a. | the first | b. | the second | c. | the
third | d. | All the electrons are equally difficult to remove. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following factors contributes to the decrease in ionization energy
within a group in the periodic table as the atomic number increases?
a. | increase in atomic size | b. | increase in size of the
nucleus | c. | increase in number of protons | d. | fewer electrons in the highest occupied energy
level |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of the following elements has the smallest first ionization energy?
a. | sodium | c. | potassium | b. | calcium | d. | magnesium |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following elements has the lowest electronegativity?
a. | lithium | c. | bromine | b. | carbon | d. | fluorine |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which statement is true about electronegativity?
a. | Electronegativity is the ability of an anion to attract another
anion. | b. | Electronegativity generally increases as you move from top to bottom within a
group. | c. | Electronegativity generally is higher for metals than for
nonmetals. | d. | Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a
period. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Compared with the electronegativities of the elements on the left side of a
period, the electronegativities of the elements on the right side of the same period tend to be
____.
a. | lower | c. | the same | b. | higher | d. | unpredictable |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following decreases with increasing atomic number in Group
2A?
a. | shielding effect | c. | ionization energy | b. | ionic size | d. | number of
electrons |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following statements correctly compares the relative size of an ion
to its neutral atom?
a. | The radius of an anion is greater than the radius of its neutral
atom. | b. | The radius of an anion is identical to the radius of its neutral
atom. | c. | The radius of a cation is greater than the radius of its neutral
atom. | d. | The radius of a cation is identical to the radius of its neutral
atom. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which of the following factors contributes to the increase in ionization energy
from left to right across a period?
a. | an increase in the shielding effect | b. | an increase in the size of the
nucleus | c. | an increase in the number of protons | d. | fewer electrons in the highest occupied energy
level |
|
|
|
29.
|
As you move from left to right across the second period of the periodic table
____.
a. | ionization energy increases | c. | electronegativity
decreases | b. | atomic radii increase | d. | atomic mass decreases |
|
|
|
30.
|
Of the following elements, which one has the smallest first ionization
energy?
a. | boron | c. | aluminum | b. | carbon | d. | silicon |
|