Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | atomic emission spectrum | d. | photon | b. | frequency | e. | quantum | c. | wavelength | f. | spectrum |
|
|
|
1.
|
discrete bundle of electromagnetic energy
|
|
|
2.
|
energy needed to move an electron from one energy level to another
|
|
|
3.
|
number of wave cycles passing a point per unit of time
|
|
|
4.
|
distance between wave crests
|
|
|
5.
|
separation of light into different wavelengths
|
|
|
6.
|
frequencies of light emitted by an element
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
7.
|
In the Bohr model of the atom, an electron in an orbit has a fixed ____.
a. | position | c. | energy | b. | color | d. | size |
|
|
|
8.
|
The shape (not the size) of an electron cloud is determined by the
electron's ____.
a. | energy sublevel | c. | speed | b. | position | d. | principal quantum
number |
|
|
|
9.
|
The letter " p" in the symbol 4 p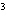 indicates
the ____. a. | spin of an electron | c. | principle energy level | b. | orbital
shape | d. | speed of an
electron |
|
|
|
10.
|
What is the electron configuration of potassium?
|
|
|
11.
|
How many unpaired electrons are in a sulfur atom (atomic number 16)?
|
|
|
12.
|
What is the wavelength of an electromagnetic wave that travels at 3 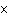
10 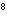 m/s and has a frequency of 60 MHz? (1 MHz = 1,000,000 Hz) a. | 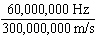 | b. | 60 MHz ´
300,000,000 m/s | c. | 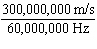 | d. | No answer can be determined from the
information given. |
|
|
|
13.
|
The light given off by an electric discharge through sodium vapor is
____.
a. | a continuous spectrum | c. | of a single wavelength | b. | an emission
spectrum | d. | white
light |
|
|
|
14.
|
Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____.
a. | drops from a higher to a lower energy level | b. | jumps from a lower
to a higher energy level | c. | moves within its atomic
orbital | d. | falls into the nucleus |
|
|
|
15.
|
As changes in energy levels of electrons increase, the frequencies of atomic
line spectra they emit ____.
a. | increase | c. | remain the same | b. | decrease | d. | cannot be
determined |
|
|
|
16.
|
The atomic emission spectra of a sodium atom on Earth and of a sodium atom in
the sun would be ____.
a. | the same | b. | different from each other | c. | the same as those of
several other elements | d. | the same as each other only in the ultraviolet
range |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the approximate energy of a photon having a frequency of 4 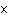
10 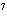 Hz? ( h = 6.6 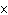 10 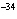 J  s)
|
|
|
18.
|
What is the approximate frequency of a photon having an energy 5 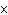 10 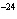 J? ( h = 6.6 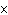 10 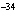 J  s)
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following quantum leaps would be associated with the greatest
energy of emitted light?
a. | n = 5 to n = 1 | c. | n = 2 to n = 5 | b. | n = 4 to n = 5 | d. | n = 5 to n = 4 |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which variable is directly proportional to frequency?
a. | wavelength | c. | position | b. | velocity | d. | energy |
|
|
|
21.
|
How do the energy differences between the higher energy levels of an atom
compare with the energy differences between the lower energy levels of the atom?
a. | They are greater in magnitude than those between lower energy
levels. | b. | They are smaller in magnitude than those between lower energy
levels. | c. | There is no significant difference in the magnitudes of these
differences. | d. | No answer can be determined from the information
given. |
|
|
|
22.
|
What are quanta of light called?
a. | charms | c. | muons | b. | excitons | d. | photons |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which scientist developed the quantum mechanical model of the atom?
a. | Albert Einstein | c. | Niels Bohr | b. | Erwin Schrodinger | d. | Ernest
Rutherford |
|
|
|
24.
|
Bohr's model could only explain the spectra of which type of atoms?
a. | single atoms with one electron | b. | bonded atoms with one
electron | c. | single atoms with more than one electron | d. | bonded atoms with
more than one electron |
|
|
|
25.
|
The quantum mechanical model of the atom ____.
a. | defines the exact path of an electron around the nucleus | b. | was proposed by
Niels Bohr | c. | involves the probability of finding an electron in a certain
position | d. | has many analogies in the visible world |
|
|
|
26.
|
Who predicted that all matter can behave as waves as well as particles?
a. | Albert Einstein | c. | Max Planck | b. | Erwin Schrodinger | d. | Louis de
Broglie |
|
|
|
27.
|
According to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, if the position of a moving
particle is known, what other quantity CANNOT be known?
a. | mass | c. | spin | b. | charge | d. | velocity |
|
|
|
28.
|
How can the position of a particle be determined?
a. | by analyzing its interactions with another particle | b. | by measuring its
velocity | c. | by measuring its mass | d. | by determining its
charge |
|
|
|
29.
|
The wavelike properties of electrons are useful in ____.
a. | defining photons | b. | writing electron
configurations | c. | magnifying objects | d. | determining the velocity and position of a
particle |
|
|
|
30.
|
In an s orbital, the probability of finding an electron a particular
distance from the nucleus does NOT depend on ____.
a. | a quantum mechanical model | c. | the Schrodinger
equation | b. | direction with respect to the nucleus | d. | the electron energy
sublevel |
|