Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | atomic orbital | d. | ground state | b. | aufbau principle | e. | Pauli exclusion principle | c. | electron
configuration | f. | Heisenberg
uncertainty principle |
|
|
|
1.
|
region of high probability of finding an electron
|
|
|
2.
|
states the impossibility of knowing both velocity and position of a moving
particle at the same time
|
|
|
3.
|
lowest energy level
|
|
|
4.
|
tendency of electrons to enter orbitals of lowest energy first
|
|
|
5.
|
arrangement of electrons around atomic nucleus
|
|
|
6.
|
each orbital has at most two electrons
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
7.
|
In Bohr's model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons
located?
a. | The electrons move around the protons, which are at the center of the
atom. | b. | The electrons and protons move throughout the atom. | c. | The electrons occupy
fixed positions around the protons, which are at the center of the atom. | d. | The electrons and
protons are located throughout the atom, but they are not free to
move. |
|
|
|
8.
|
In the Bohr model of the atom, an electron in an orbit has a fixed ____.
a. | position | c. | energy | b. | color | d. | size |
|
|
|
9.
|
How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the
nucleus?
a. | It decreases. | c. | It stays the same. | b. | It increases. | d. | It doubles. |
|
|
|
10.
|
The principal quantum number indicates what property of an electron?
a. | position | c. | energy level | b. | speed | d. | electron cloud
shape |
|
|
|
11.
|
What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital?
a. | sphere | c. | bar | b. | dumbbell | d. | two perpendicular
dumbbells |
|
|
|
12.
|
How many energy sublevels are in the second principal energy level?
|
|
|
13.
|
What is the maximum number of f orbitals in any single energy level in an
atom?
|
|
|
14.
|
What is the maximum number of d orbitals in a principal energy
level?
|
|
|
15.
|
What is the maximum number of orbitals in the p sublevel?
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the maximum number of electrons in the second principal energy
level?
|
|
|
17.
|
When an electron moves from a lower to a higher energy level, the electron
____.
a. | always doubles its energy | b. | absorbs a continuously variable amount of
energy | c. | absorbs a quantum of energy | d. | moves closer to the
nucleus |
|
|
|
18.
|
The shape (not the size) of an electron cloud is determined by the
electron's ____.
a. | energy sublevel | c. | speed | b. | position | d. | principal quantum
number |
|
|
|
19.
|
The letter " p" in the symbol 4 p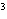 indicates
the ____. a. | spin of an electron | c. | principle energy level | b. | orbital
shape | d. | speed of an
electron |
|
|
|
20.
|
If the spin of one electron in an orbital is clockwise, what is the spin of the
other electron in that orbital?
a. | zero | c. | counterclockwise | b. | clockwise | d. | both clockwise and
counterclockwise |
|
|
|
21.
|
What types of atomic orbitals are in the third principal energy level?
a. | s and p only | c. | s, p, and d
only | b. | p and d only | d. | s, p, d, and f |
|
|
|
22.
|
What is the next atomic orbital in the series 1s, 2s, 2p,
3s, 3p?
|
|
|
23.
|
According to the aufbau principle, ____.
a. | an orbital may be occupied by only two electrons | b. | electrons in the
same orbital must have opposite spins | c. | electrons enter orbitals of highest energy
first | d. | electrons enter orbitals of lowest energy first |
|
|
|
24.
|
What is the number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an oxygen
atom?
|
|
|
25.
|
What is the electron configuration of potassium?
|
|
|
26.
|
If three electrons are available to fill three empty 2p atomic orbitals,
how will the electrons be distributed in the three orbitals?
a. | one electron in each orbital | b. | two electrons in one orbital, one in another,
none in the third | c. | three in one orbital, none in the other
two | d. | Three electrons cannot fill three empty 2p atomic
orbitals. |
|
|
|
27.
|
How many unpaired electrons are in a sulfur atom (atomic number 16)?
|
Numeric Response
|
|
|
28.
|
How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of a neutral
chlorine atom?
|
|
|
29.
|
How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of a neutral
strontium atom?
|
|
|
30.
|
How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of copper?
|