Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
An element has an atomic number of 76. The number of protons and electrons in a
neutral atom of the element are ____.
a. | 152 protons and 76 electrons | c. | 38 protons and 38
electrons | b. | 76 protons and 0 electrons | d. | 76 protons and 76 electrons |
|
|
|
2.
|
An element has an atomic number of 10. The number of protons and electrons in a
neutral atom of the element are ____.
a. | 20 protons and 10 electrons | c. | 5 protons and 5
electrons | b. | 10 protons and 0 electrons | d. | 10 protons and 10 electrons |
|
|
|
3.
|
An element has an atomic number of 20. The number of protons and electrons in a
neutral atom of the element are ____.
a. | 20 protons and 20 electrons | c. | 10 protons and 10
electrons | b. | 20 protons and 0 electrons | d. | 40 protons and 20 electrons |
|
|
|
4.
|
An element has an atomic number of 44. The number of protons and electrons in a
neutral atom of the element are ____.
a. | 44 protons and 44 electrons | c. | 44 protons and 0
electrons | b. | 88 protons and 44 electrons | d. | 22 protons and 22 electrons |
|
|
|
5.
|
An element has an atomic number of 58. The number of protons and electrons in a
neutral atom of the element are ____.
a. | 58 protons and 58 electrons | c. | 29 protons and 29
electrons | b. | 116 protons and 58 electrons | d. | 58 protons and 0
electrons |
|
|
|
6.
|
An element has an atomic number of 42. The number of protons and electrons in a
neutral atom of the element are ____.
a. | 42 protons and 42 electrons | c. | 21 protons and 21
electrons | b. | 84 protons and 42 electrons | d. | 42 protons and 0 electrons |
|
|
|
7.
|
An element has an atomic number of 34. The number of protons and electrons in a
neutral atom of the element are ____.
a. | 17 protons and 17 electrons | c. | 34 protons and 0
electrons | b. | 68 protons and 34 electrons | d. | 34 protons and 34 electrons |
|
|
|
8.
|
An element has an atomic number of 12. The number of protons and electrons in a
neutral atom of the element are ____.
a. | 12 protons and 0 electrons | c. | 6 protons and 6
electrons | b. | 12 protons and 12 electrons | d. | 24 protons and 12 electrons |
|
|
|
9.
|
The mass number of an element is equal to ____.
a. | the total number of electrons in the nucleus | b. | the total number of
protons and neutrons in the nucleus | c. | less than twice the atomic
number | d. | a constant number for the lighter elements |
|
|
|
10.
|
In which of the following is the number of neutrons correctly
represented?
a. | 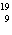 F has 0 neutrons. F has 0 neutrons. | c. | 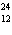 Mg has 24
neutrons. Mg has 24
neutrons. | b. | 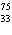 As has 108 neutrons. As has 108 neutrons. | d. | 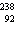 U has 146
neutrons. U has 146
neutrons. |
|
|
|
11.
|
How do the isotopes hydrogen-1 and hydrogen-2 differ?
a. | Hydrogen-2 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. | b. | Hydrogen-2 has one
neutron; hydrogen-1 has none. | c. | Hydrogen-2 has two protons; hydrogen-1 has
one. | d. | Hydrogen-2 has one proton; hydrogen-1 has none. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following isotopes has the same number of neutrons as
phosphorus-31?
|
|
|
13.
|
What unit is used to measure weighted average atomic mass?
a. | amu | c. | angstrom | b. | gram | d. | nanogram |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following equals one atomic mass unit?
a. | the mass of one electron | b. | the mass of one helium-4
atom | c. | the mass of one carbon-12 atom | d. | one-twelfth the mass of one carbon-12
atom |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
a. | Protons have a positive charge. | b. | Electrons are negatively charged and have a
mass of 1 amu. | c. | The nucleus of an atom is positively charged. | d. | Neutrons are located
in the nucleus of an atom. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Why do chemists use relative masses of atoms compared to a reference isotope
rather than the actual masses of the atoms?
a. | The actual mass of an electron is very large compared to the actual mass of a
proton. | b. | The actual masses of atoms are very small and difficult to work
with. | c. | The number of subatomic particles in atoms of different elements
varies. | d. | The actual masses of protons, electrons, and neutrons are not
known. |
|
|
|
17.
|
The atomic mass of an element is the ____.
a. | total number of subatomic particles in its nucleus | b. | weighted average of
the masses of the isotopes of the element | c. | total mass of the isotopes of the
element | d. | average of the mass number and the atomic number for the
element |
|
|
|
18.
|
The atomic mass of an element depends upon the ____.
a. | mass of each electron in that element | b. | mass of each isotope of that
element | c. | relative abundance of protons in that element | d. | mass and relative
abundance of each isotope of that element |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following is necessary to calculate the atomic mass of an
element?
a. | the atomic mass of carbon-12 | b. | the atomic number of the
element | c. | the relative masses of the element’s protons and neutrons | d. | the masses of each
isotope of the element |
|
Numeric Response
|
|
|
20.
|
What is the atomic number for an element with 41 neutrons and a mass number of
80?
|
|
|
21.
|
What is the atomic number for an element with 38 neutrons and a mass number of
74?
|
|
|
22.
|
What is the atomic number for an element with 46 neutrons and a mass number of
90?
|
|
|
23.
|
What is the atomic number for an element with 43 neutrons and a mass number of
84?
|
|
|
24.
|
What is the atomic number for an element with 44 neutrons and a mass number of
86?
|
|
|
25.
|
What is the atomic number for an element with 36 neutrons and a mass number of
70?
|
|
|
26.
|
What is the mass number for an oxygen atom that has 10 neutrons in its
nucleus?
|
|
|
27.
|
How many protons are present in the nuclei of the three known isotopes of
hydrogen?
|
|
|
28.
|
Use the periodic table to determine the number of neutrons in
nitrogen-14.
|
|
|
29.
|
How many neutrons are present in an atom of the isotope 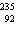 U?
|
|
|
30.
|
Calculate the number of neutrons in 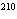 Pb.
|