Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | positron | d. | transuranium element | b. | alpha particle | e. | gamma radiation | c. | beta
particle | f. | transmutation |
|
|
|
1.
|
element with atomic number greater than 92
|
|
|
2.
|
emitted helium nucleus
|
|
|
3.
|
energetic electron from decomposed neutron
|
|
|
4.
|
high-energy photons emitted by a radioisotope
|
|
|
5.
|
particle of charge +1 and mass equal to that of an electron
|
|
|
6.
|
conversion of an atom of one element to an atom of another element
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | fission | e. | scintillation counter | b. | fusion | f. | neutron absorption | c. | Geiger counter | g. | neutron moderation | d. | radioisotope |
|
|
|
7.
|
element with unstable nucleus
|
|
|
8.
|
combination of two nuclei to form a nucleus of greater mass
|
|
|
9.
|
process that decreases the number of slow-moving neutrons
|
|
|
10.
|
splitting of nucleus into smaller fragments
|
|
|
11.
|
process that slows down neutrons so a reactor fuel can capture them to continue
a chain reaction
|
|
|
12.
|
radiation detector that makes use of a phosphor-coated surface
|
|
|
13.
|
radiation detector that makes use of a gas-filled metal tube
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
14.
|
An unstable nucleus ____.
a. | increases its nuclear mass by fission | c. | emits energy when it
decays | b. | increases its half-life | d. | expels all of its protons |
|
|
|
15.
|
The charge on a gamma ray is ____.
a. | +2 | c. | 0 | b. | 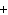 1 1 | d. |  2 2 |
|
|
|
16.
|
The charge on an alpha particle is ____.
a. |  2 2 | c. | -1 | b. | +2 | d. | 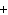 1 1 |
|
|
|
17.
|
The charge on a beta particle is ____.
a. | +2 | c. | -1 | b. | 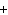 1 1 | d. |  2 2 |
|
|
|
18.
|
What particle is emitted in alpha radiation?
a. | electron | c. | helium nucleus | b. | photon | d. | hydrogen
nucleus |
|
|
|
19.
|
A beta particle is a(n) ____.
a. | photon | c. | helium nucleus | b. | electron | d. | hydrogen
nucleus |
|
|
|
20.
|
What is the change in atomic mass when an atom emits a beta particle?
a. | decreases by 2 | c. | remains the same | b. | decreases by 1 | d. | increases by 1 |
|
|
|
21.
|
What is the change in atomic mass when an atom emits gamma radiation?
a. | decreases by 2 | c. | remains the same | b. | decreases by 1 | d. | increases by 1 |
|
|
|
22.
|
The least penetrating form of radiation is ____.
a. | beta radiation | c. | alpha radiation | b. | gamma radiation | d. | X rays |
|
|
|
23.
|
What is the change in the atomic number when an atom emits an alpha
particle?
a. | decreases by 2 | c. | increases by 1 | b. | decreases by 1 | d. | increases by 2 |
|
|
|
24.
|
What is the change in atomic number when an atom emits a beta particle?
a. | decreases by 2 | c. | increases by 2 | b. | decreases by 1 | d. | increases by 1 |
|
|
|
25.
|
What is the change in atomic number caused by the emission of gamma
radiation?
a. | decreases by 2 | c. | remains the same | b. | decreases by 1 | d. | increases by 1 |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which symbol is used for an alpha particle?
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following materials is necessary to stop an alpha particle?
a. | three feet of concrete | c. | single sheet of aluminum foil | b. | three inches of
lead | d. | single sheet of
paper |
|
|
|
28.
|
What particle decomposes to produce the electron of beta radiation?
a. | proton | c. | electron | b. | neutron | d. | positron |
|
|
|
29.
|
What symbol is used for beta radiation?
|
|
|
30.
|
What particle is needed to complete this nuclear reaction? 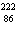 Rn 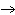 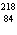 Po + _____
|
|
|
31.
|
When radium-226 (atomic number 88) decays by emitting an alpha particle, it
becomes ____.
a. | polonium-222 | c. | radium-222 | b. | polonium-224 | d. | radon-222 |
|
|
|
32.
|
What particle is needed to complete the following nuclear equation? 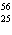 Mn  ____ + 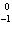 e
|
|
|
33.
|
What particle is needed to complete the following equation? 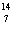 N + ____
 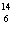 C + 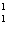 H
|
|
|
34.
|
What is the approximate half-life of uranium-238?
a. | hundreds of years | c. | millions of years | b. | thousands of years | d. | billions of
years |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following naturally occurring radioisotopes would be most useful in
dating objects thought to be millions of years old?
|
|
|
36.
|
What happens in a chain reaction?
a. | Products that start a new reaction are released. | b. | Reactants that have
two parts split. | c. | Products that are radioactive are lost. | d. | Radioactive
reactants are deposited on control rods. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Nuclear fusion ____.
a. | takes place in the sun | c. | can be controlled in the laboratory | b. | occurs at low
temperatures | d. | is used in
medicine |
|
|
|
38.
|
What instrument is used routinely to check a person's exposure to
radiation?
a. | Geiger counter | c. | film badge | b. | scintillation counter | d. | moderating rod |
|
|
|
39.
|
Radiation therapy is used to ____.
a. | study reaction mechanisms | c. | treat cancer | b. | detect
elements | d. | initiate neutron
activation analysis |
|
|
|
40.
|
Radioisotopes taken internally for medical reasons ____.
a. | must be eliminated from the body slowly | b. | should be
fissionable isotopes | c. | are usually deposited in fat
tissue | d. | should have a short half-life |
|