Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The SI unit of force is the
a. | joule. | c. | meter. | b. | kilogram. | d. | newton. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which of the following relationships is correct?
a. | 1 N = 1 kg | c. | 1 N = 1 kg·m/s | b. | 1 N = 1 kg·m | d. | 1 N = 1
kg·m/s2 |
|
|
|
3.
|
When an unbalanced force acts on an object,
a. | the object’s motion does not change. | c. | the weight of the object
decreases. | b. | the object accelerates. | d. | the inertia of the object increases. |
|
|
|
4.
|
When a pair of balanced forces acts on an object, the net force that results
is
a. | greater in size than both forces combined. | b. | greater in size than
one of the forces. | c. | equal in size to one of the
forces. | d. | equal to zero. |
|
|
|
5.
|
What kind of friction occurs as a fish swims through water?
a. | fluid | c. | sliding | b. | rolling | d. | static |
|
|
|
6.
|
As you push a cereal box across a tabletop, the sliding friction acting on the
cereal box
a. | acts in the direction of motion. | b. | equals the weight of the
box. | c. | is usually greater than static friction. | d. | acts in the
direction opposite of motion. |
|
|
|
7.
|
The forces acting on a falling leaf are
a. | air resistance and fluid friction. | c. | gravity and static
friction. | b. | gravity and air resistance. | d. | weight and rolling friction. |
|
|
|
8.
|
An open parachute increases air resistance of a falling sky diver by
a. | decreasing the weight of the diver. | c. | increasing the terminal
velocity. | b. | increasing surface area. | d. | reducing fluid friction. |
|
|
|
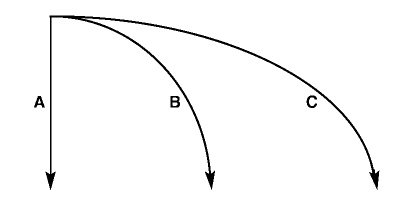
Figure 12-1
|
|
|
9.
|
Figure 12-1 shows the motion of three balls. The curved paths followed by balls
B and C are examples of
a. | centripetal motion. | c. | linear motion. | b. | constant motion. | d. | projectile
motion. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Projectile motion is caused by
a. | the downward force of gravity. | b. | an initial forward
velocity. | c. | a final vertical velocity. | d. | the downward force of gravity and an initial
forward velocity. |
|
|
|
11.
|
The property of matter that resists changes in motion is called
a. | friction. | c. | inertia. | b. | gravity. | d. | weight. |
|
|
|
12.
|
An orange might roll off your cafeteria tray when you stop suddenly because
of
a. | the balanced forces acting on the orange. | b. | the centripetal
force acting on the orange. | c. | the friction forces acting on the
orange. | d. | the orange’s inertia. |
|
|
|
13.
|
According to Newton’s second law of motion, the acceleration of an object
equals the net force acting on the object divided by the object’s
a. | mass. | c. | velocity. | b. | momentum. | d. | weight. |
|
|
|
14.
|
If a force of 12 N is applied to an object with a mass of 2 kg, the object will
accelerate at
a. | 0.17 m/s2. | c. | 6 m/s2. | b. | 24 m/s2. | d. | 12
m/s2. |
|
|
|
15.
|
Your weight equals your
a. | mass. | b. | mass divided by the net force acting on
you. | c. | mass times the acceleration due to gravity. | d. | mass times your
speed. |
|
|
|
16.
|
The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Mars is about one third the
acceleration due to gravity on Earth’s surface. The weight of a space probe on the surface of
Mars is about
a. | nine times greater than its weight on Earth’s surface. | b. | three times greater
than its weight on Earth’s surface. | c. | one third its weight on Earth’s
surface. | d. | the same as its weight on Earth’s surface. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Newton’s third law of motion describes
a. | action and reaction forces. | c. | centripetal
forces. | b. | balanced forces. | d. | net force. |
|
|
|
18.
|
In which of the following are action and reaction forces involved?
a. | when a tennis racket strikes a tennis ball | b. | when stepping from a
curb | c. | when rowing a boat | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
19.
|
The product of an object’s mass and velocity is its
a. | centripetal force. | c. | net force. | b. | momentum. | d. | weight. |
|
|
|
20.
|
What is conserved when two objects collide in a closed system?
a. | acceleration | c. | speed | b. | momentum | d. | velocity |
|
|
|
21.
|
What is the momentum of a 50-kilogram ice skater gliding across the ice at a
speed of 5 m/s?
a. | 10 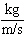 | c. | 50 kg | b. | 500
kg·m/s | d. | 250
kg·m/s |
|
|
|
22.
|
What force is responsible for the repulsion between two positively-charged
particles?
a. | centripetal | c. | gravitational | b. | electric | d. | nuclear |
|
|
|
23.
|
When opposite poles of two magnets are brought together, the poles
a. | attract each other. | c. | cancel each other. | b. | repel each other. | d. | cause a net force of
zero. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which universal force acts only on the protons and neutrons in a nucleus?
a. | electric | c. | magnetic | b. | gravitational | d. | strong nuclear |
|
|
|
25.
|
With which of the following is the weak nuclear force associated?
a. | lightning | c. | ocean tides | b. | nuclear decay | d. | static cling |
|