Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The SI unit for speed is
a. | mph. | c. | m/s. | b. | ft/s2. | d. | Dv /
t. |
|
|
|
2.
|
On a speed-time graph, a line with a negative slope indicates that the object
is
a. | speeding up. | c. | not moving. | b. | slowing down. | d. | traveling at a constant
speed. |
|
|
|
3.
|
The combination of all of the forces acting on an object is called the
a. | total force. | c. | super force. | b. | union of forces. | d. | net force. |
|
|
|
4.
|
If the net force acting on a stationary object is zero, then the object
will
a. | accelerate in the direction of the strongest force. | b. | remain at
rest. | c. | begin moving backwards. | d. | decelerate at a steady rate of
speed. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Average speed can be represented by the mathematical expression
a. | distance/time. | c. | time –
distance. | b. | distance ´ time. | d. | time +
distance. |
|
|
|
6.
|
The _____ of an object consists of its speed and direction.
a. | velocity | c. | average speed | b. | instantaneous speed | d. | displacement |
|
|
|
7.
|
The average speed of a runner who runs 500.0 m in 1.6 min is
a. | 0.19 m/s. | c. | 96 m/s. | b. | 5.2 m/s. | d. | 312 m/s. |
|
|
|
8.
|
A car moving at an average speed of 55.0 mi/h for 4.25 h has traveled
a. | 0.08 mi. | c. | 55 mi. | b. | 13 mi. | d. | 234 mi. |
|
|
|
9.
|
On a distance vs. time graph of an object’s motion, distance is
usually
a. | plotted on the x-axis. | c. | the dependent
variable. | b. | greater than time. | d. | measured in ft/min. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Displacement must always indicate
a. | velocity. | c. | speed. | b. | direction. | d. | time. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Speeding up, slowing down, and changing direction is best described as
a. | velocity. | c. | displacement. | b. | distance. | d. | acceleration. |
|
|
|
12.
|
The equation for finding average acceleration for straight-line motion is
a. | initial velocity – final velocity ´
time. | b. | final velocity – initial velocity/time. | c. | initial velocity +
final velocity + time. | d. | initial velocity + final velocity –
time. |
|
|
|
13.
|
On a velocity vs. time graph, what shows the value of the acceleration?
a. | the slope of the line | c. | the y-axis | b. | the x-axis | d. | the final
velocity |
|
|
|
14.
|
On a distance vs. time graph, the line of an object at rest is a
a. | curved line with a slope of zero. | c. | jagged line with a negative
slope. | b. | flat line with a slope of zero. | d. | curved line with a positive
slope. |
|
|
|
15.
|
The difference between speed and velocity is that velocity includes
a. | direction. | c. | time. | b. | distance. | d. | weight. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Friction is defined as the
a. | force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. | b. | rate at which
velocity changes. | c. | resistance of an object to a change in its
velocity. | d. | speed of an object in a particular direction. |
|
|
|
17.
|
On a speed vs. time graph, constant acceleration is represented by a
a. | straight line. | c. | jagged line. | b. | slightly sloped line. | d. | steeply sloped
line. |
|
|
|
18.
|
The law that states that every object maintains constant velocity unless acted
on by an unbalanced force is
a. | Newton’s first law of motion. | b. | Newton’s second law of
motion. | c. | Newton’s third law of motion. | d. | the law of conservation of
momentum. |
|
|
|
19.
|
The law that states that for every action force there is an equal and opposite
reaction force is
a. | Newton’s first law of motion. | b. | Newton’s second law of
motion. | c. | Newton’s third law of motion. | d. | the law of conservation of
momentum. |
|
|
|
20.
|
The law that states that the unbalanced force acting on an object equals the
object’s mass times its acceleration is
a. | Newton’s first law of motion. | b. | Newton’s second law of
motion. | c. | Newton’s third law of motion. | d. | the law of conservation of
momentum. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following equations is correct?
a. | w = mg | c. | w = g/m | b. | w = m/g | d. | w = g + m |
|
|
|
22.
|
Express the following as an equation: One newton is the force that can give an
object with a mass of 1 kg an acceleration of 1 m/s2.
a. | 1 N = 1 kg ÷ 1 m/s2 | c. | 1 N = 1 m/s2 ÷ 1
kg | b. | 1 N ´ 1 kg = 1 m/s2 | d. | 1 N = 1 kg ´ 1
m/s2 |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which object has the greatest inertia?
a. | a tennis ball | c. | a beach ball | b. | a bowling ball | d. | a volleyball |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following will result in the greatest acceleration?
a. | 56 N acting on a 1-kg box | c. | 23 N acting on a 2-kg
box | b. | 56 N acting on a 2-kg box | d. | 23 N acting on a 5-kg box |
|
|
|
25.
|
A force of 240.0 N causes an object to accelerate at 3.2 m/s2. What
is the mass of the object?
a. | 0.013 kg | c. | 240 kg | b. | 75 kg | d. | 768 kg |
|
|
|
26.
|
If an equal force is applied to two cars of equal mass, Car A and Car B, Car A
will have _____ acceleration as (than) Car B.
a. | the same | c. | less | b. | greater | d. | the opposite |
|
|
|
27.
|
How much does a 59.0 kg woman weigh on Earth?
a. | 6.02 N | c. | 145 lb | b. | 59.0 lb | d. | 578 N |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which is an example of projectile motion?
a. | a rolling bowling ball | c. | a balloon rising in the air | b. | a dart thrown at a
dart board | d. | a high-speed
train accelerating |
|
|
|
29.
|
An object’s momentum is determined by the object’s
a. | weight and velocity. | c. | mass and velocity. | b. | mass and acceleration. | d. | weight and
acceleration. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Calculate the velocity of a 90.5 kg man running south with a momentum of 389 kg
• m/s.
a. | 0.233 m/s south | c. | 23.3 m/s south | b. | 4.30 m/s south | d. | 35.2 m/s south |
|
|
|
31.
|
The SI unit of force, named after the scientist who described the relationship
between motion and force, is called the
a. | newton. | c. | curie. | b. | einstein. | d. | pasteur |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of the following units is used to measure acceleration?
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the following is true?
a. | Weight and mass are proportional but not equal. | b. | Weight is
gravitational force an object experiences due to its mass. | c. | The weight of an
object on Earth is greater than the weight of the same object on the moon, but the object’s
mass stays the same. | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
34.
|
The tendency of an object at rest to remain at rest is
a. | inertia. | c. | free fall. | b. | momentum. | d. | acceleration. |
|
|
|
35.
|
The transfer of energy to a body by the application of a force that causes the
body to move in the direction of the force is called
a. | power. | c. | distance. | b. | work. | d. | mechanical
advantage |
|
|
|
36.
|
A boy exerts an average force of 65 N when he lifts a box 1.2 meters. How much
work does he do?
|
|
|
37.
|
_____ is defined as the rate at which work is done.
a. | Power | c. | Speed | b. | Joule | d. | Mechanical
advantage |
|
|
|
38.
|
How much power is required to do 180 J of work in 2.4 s?
a. | 7.5 W | c. | 178 W | b. | 75 W | d. | 430 W |
|
|
|
39.
|
How much power is required to lift a 30.0 N chair 0.20 m in 2.0 s?
a. | 1.0 W | c. | 12 W | b. | 3.0 W | d. | 15 W |
|
|
|
40.
|
A pulley with a mechanical advantage of 5.00 is used to lift a bucket weighing
285 N. How much force must be used to lift the bucket?
a. | 57.0 N | c. | 285 N | b. | 280 N | d. | 1,425 N |
|
|
|
41.
|
Lifting a car using a car jack is easier because it requires
a. | less force. | c. | less time. | b. | less work. | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
42.
|
_____ is a measure of the ability to do work.
a. | Photosynthesis | c. | Respiration | b. | Power | d. | Energy |
|
|
|
43.
|
Calculate the gravitational potential energy relative to the ground when an 82
kg person climbs to the top of a 2.0 m stepladder.
a. | 164 J | c. | 402 J | b. | 3.3 ´
102 J | d. | 1.6 ´ 103 J |
|
|
|
44.
|
What is the kinetic energy of a 1.40 kg discus with a speed of 22.5 m/s?
a. | 15.8 J | c. | 354 J | b. | 31.5 J | d. | 709 J |
|
|
|
45.
|
A dog running at a speed of 12 m/s has 1,080 J of kinetic energy. What is the
mass of the dog?
a. | 7.5 kg | c. | 30 kg | b. | 15 kg | d. | 45 kg |
|
|
|
46.
|
The law of conservation of energy states that energy
a. | is created from motion. | c. | is always equal and
opposite. | b. | cannot be created or destroyed. | d. | can only be converted into
heat. |
|
|
|
47.
|
_____ is the ratio of useful work output to work input.
a. | Potential energy | c. | Kinetic energy | b. | Efficiency | d. | Power |
|
|
|
48.
|
What are the units of work?
a. | J | c. | kg • m2/s2 | b. | N • m | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
49.
|
A machine is a device that
a. | requires less work to do a given task. | b. | decreases the amount of work done by a given
force. | c. | increases energy. | d. | can multiply and change the direction of an
input force. |
|
|
|
50.
|
What is the gravitational potential energy of a 54 kg box that is 8.0 m above
the ground?
a. | 5,500 J | c. | 3,400 J | b. | 4,300 J | d. | 550 J |
|
|
|
51.
|
What are the units of power?
a. | watts | c. | joules per second | b. | horsepower | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
52.
|
Gravitational potential energy depends on
a. | the mass of the object. | c. | the acceleration due to
gravity. | b. | the height of the object. | d. | All of the above |
|
|
|
53.
|
A medicine ball has a mass of 5 kg and is thrown with a speed of 2 m/s. What is
its kinetic energy?
a. | 100 J | c. | 2,000 J | b. | 10 J | d. | 500 J |
|
|
|
54.
|
According to the first law of thermodynamics,
a. | there is no such thing as a perpetual motion machine. | b. | the energy of a
system is constant. | c. | the total energy used in any process is
conserved. | d. | in any process there is a decrease in potential
energy. |
|
|
|
55.
|
The Fahrenheit temperature scale is defined by which of the following
temperatures?
a. | Water boils at 100 degrees and freezes at 32 degrees. | b. | Water boils at 212
degrees and freezes at 32 degrees. | c. | Water evaporates at 212 degrees and freezes at
0 degrees. | d. | Liquid water turns to a gas at 100 degrees and to a solid at 0
degrees. |
|
|
|
56.
|
Temperature is a measure of the average _____ energy of an object’s
particles.
a. | mechanical | c. | potential | b. | kinetic | d. | light |
|
|
|
57.
|
Which of the following is the name of a temperature scale?
a. | Celsius | c. | Kelvin | b. | Fahrenheit | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
58.
|
The temperature at which all molecular motion stops is
a. | 0°C. | c. | 0 K. | b. | 0°F. | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
59.
|
Calculate the energy transferred when raising the temperature of 16 kg of water
by 3°C (c = 4,186 J/kg • K).
a. | 785 J | c. | 1.26 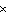 105 J 105 J | b. | 2.2
kJ | d. | 2.0 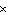 105 J
105 J |
|
|
|
60.
|
Calculate the specific heat for a 20 g piece of metal if 30 J of energy is
required to raise its temperature by 12.5 K.
a. | 0.12 J/kg • K | c. | 120 J/kg • K | b. | 7.5 J/kg • K | d. | 48 kJ/kg •
K |
|
|
|
61.
|
As the kinetic energy of the molecules in a substance increases, the
a. | temperature of the substance increases. | b. | temperature of the
substance decreases. | c. | potential energy of the substance
changes. | d. | temperature remains the same. |
|
|
|
62.
|
The temperature of a substance increases by 3 K when 1,635 J is added to a 2 kg
quantity of the substance. What is the specific heat of the substance?
a. | 242 J/kg • K | c. | 300 J/kg • K | b. | 272 J/kg • K | d. | 817 J/kg •
K |
|
|
|
63.
|
The temperature of 1.5 kg of ethanol is 37°C. What will the final
temperature be if 80,000 J of energy as heat is added to the ethanol?
|
|
|
64.
|
What is –175°C on the Kelvin scale?
a. | 76 K | c. | 98 K | b. | 89 K | d. | 448 K |
|
|
|
65.
|
SPECIFIC HEATS AT 25° C
Substance | c (J/kg • K) | Substance | c (J/kg • K) | | Water (liquid) | 4,186 | Copper | 385 | | Steam | 1,870 | Gold | 129 | | Ammonia (gas) | 2,060 | Iron | 449 | | Ethanol (liquid) | 2,440 | Mercury | 140 | | Aluminum | 897 | Lead | 129 | | Carbon (graphite) | 709 | Silver | 234 | | | | |
Which substance listed in the table above has a specific heat
approximately 10 times greater than the specific heat of silver?
a. | water | c. | carbon | b. | ethanol | d. | mercury |
|
|
|
66.
|
The _____ of a longitudinal wave radiates outward from its source, while the
particles vibrate back and forth about their original positions.
a. | medium | c. | crest | b. | wave front | d. | kinetic energy |
|
|
|
67.
|
The maximum displacement of a particle by a wave is called
a. | amplitude. | c. | frequency. | b. | wavelength. | d. | period. |
|
|
|
68.
|
The _____ is the distance between two crests of a wave.
a. | amplitude | c. | frequency | b. | wavelength | d. | period |
|
|
|
69.
|
The _____ is the time it takes for one full vibration of a particle in a
medium.
a. | period | c. | amplitude | b. | frequency | d. | wave speed |
|
|
|
70.
|
_____ is the inverse of period.
a. | Wavelength | c. | Frequency | b. | Crest | d. | Amplitude |
|
|
|
71.
|
Calculate the wave speed for a wave with a wavelength of 2 m and a frequency of
0.3 Hz.
a. | 0.6 m/s | c. | 0.15 m/s | b. | 1.67 m/s | d. | 2.3 m/s |
|
|
|
72.
|
What is the period of a wave with a wave speed of 50 m/s and a wavelength of 10
mm?
a. | 2 s | c. | 0.02 s | b. | 0.2 s | d. | 0.0002 s |
|
|
|
73.
|
The Doppler effect is an observed change in a wave’s
a. | wavelength. | c. | amplitude. | b. | period. | d. | frequency. |
|
|
|
74.
|
The amplitude of the
wave in the diagram above is a. | 6 m. | c. | 0.5 m. | b. | 3 m. | d. | 1 m. |
|
|
|
75.
|
The wavelength of the
wave in the diagram above is a. | 6.0 m. | c. | 3 m. | b. | 1.5 m. | d. | 0.75 m. |
|
|
|
76.
|
A train of waves is moving at a speed of 30 m/s. The frequency of the waves is
10 Hz. What is the wavelength?
a. | 300 m | c. | 3 m | b. | 30 m | d. | 0.1 m |
|
|
|
77.
|
A wave with a frequency of 0.5 Hz and a speed of 10 m/s has a wavelength
of
a. | 50 m. | c. | 20 m. | b. | 0.5 m. | d. | 0.2 m. |
|
|
|
78.
|
The pitch of a sound is most closely related to the
a. | frequency of the sound waves. | b. | distance from the sound
source. | c. | medium through which the sound travels. | d. | intensity of the
sound. |
|
|
|
79.
|
The rate at which energy flows through a given
space describes light a. | resonance. | c. | intensity. | b. | pitch. | d. | interference. |
|
|
|
80.
|
The law of reflection says the angle of incidence is _____ the angle of
reflection.
a. | greater than | c. | equal to | b. | less than | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
81.
|
A virtual image
a. | appears in front of a mirror. | c. | diffuses light. | b. | appears behind a
mirror. | d. | reflects
light. |
|
|
|
82.
|
When all three additive primary colors are mixed, you see the color
a. | black. | c. | cyan. | b. | magenta. | d. | white. |
|
|
|
83.
|
A mirage is caused by
a. | dispersing light. | c. | diverging light. | b. | converging light. | d. | refracting
light. |
|
|
|
84.
|
The amount of energy in a photon of light is proportional to the
a. | medium through which it travels. | b. | shape of the light wave it
creates. | c. | speed of the corresponding light wave. | d. | frequency of the corresponding light
wave. |
|
|
|
85.
|
The effect in which white light separates into different colors is called
a. | magnification. | c. | reflection. | b. | refraction. | d. | dispersion. |
|
|
|
86.
|
Appliances connected so that they form a single pathway for charges to flow are
connected in a(n)
a. | series circuit. | c. | open circuit. | b. | parallel circuit. | d. | closed circuit. |
|
|
|
87.
|
Which of the following is a negatively charged particle?
a. | proton | c. | coulomb | b. | electron | d. | neutron |
|
|
|
88.
|
_____ is the opposition posed by a material to the flow of current.
a. | Voltage | c. | Resistance | b. | Charge | d. | Ampere |
|
|
|
89.
|
Current is produced when charges are accelerated by an electric field to move to
a position of lower
a. | temperature. | c. | concentration. | b. | potential energy. | d. | kinetic energy. |
|
|
|
90.
|
Calculate the resistance of a bulb that draws 0.6 A of current with a potential
difference of 3 V.
a. | 0.2 W | c. | 5 W | b. | 1.8 W | d. | 15
W |
|
|
|
91.
|
A 6.0-V battery is connected to a 24-W resistor. What
is the current in the resistor?
a. | 0.25 A | c. | 18 A | b. | 4.0 A | d. | 144 A |
|
|
|
92.
|
A device connected to a 120-V outlet has 2.0 A of current in it. What is the
power of this device?
a. | 48 W | c. | 240 W | b. | 60 W | d. | 480 W |
|
|
|
93.
|
A circuit breaker acts as a switch creating a(n) _____ circuit when current is
too high.
a. | closed | c. | open | b. | series | d. | parallel |
|
|
|
94.
|
What voltage is required to pass 0.5 A of current through a 4.5-W bulb?
a. | 0.11 V | c. | 3 V | b. | 2.25 V | d. | 9 V |
|
|
|
95.
|
The SI unit of resistance is the
a. | volt. | c. | ohm. | b. | ampere. | d. | joule. |
|
|
|
96.
|
A resistor has a resistance of 280 W. How much
current is in the resistor if there is a potential difference of 120 V across the resistor?
a. | 160 A | c. | 0.12 A | b. | 0.43 A | d. | 2.3 A |
|
|
|
97.
|
A microwave draws 5.0 A when it is connected to a 120-V outlet. If electrical
energy costs $0.090/kW • h, what is the cost of running the microwave for exactly 6
hours?
a. | $2.70 | c. | $0.72 | b. | $1.60 | d. | $0.32 |
|
|
|
98.
|
Potential difference is measured in
a. | amperes. | c. | coulombs. | b. | volts. | d. | joules. |
|
|
|
99.
|
A flashlight bulb with a potential difference of 4.5 V across its filament has a
power output of 8.0 W. How much current is in the bulb filament?
a. | 3.7 A | c. | 0.23 A | b. | 1.8 A | d. | 0.56 A |
|
|
|
100.
|
A 13-W resistor has 0.050 A of current in it. What is
the potential difference across the resistor?
a. | 6.5 V | c. | 0.065 V | b. | 0.65 V | d. | 0.0065 V |
|