Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
According to the first law of thermodynamics,
a. | there is no such thing as a perpetual motion machine. | b. | the energy of a
system is constant. | c. | the total energy used in any process is
conserved. | d. | in any process there is a decrease in potential
energy. |
|
|
|
2.
|
The Fahrenheit temperature scale is defined by which of the following
temperatures?
a. | Water boils at 100 degrees and freezes at 32 degrees. | b. | Water boils at 212
degrees and freezes at 32 degrees. | c. | Water evaporates at 212 degrees and freezes at
0 degrees. | d. | Liquid water turns to a gas at 100 degrees and to a solid at 0
degrees. |
|
|
|
3.
|
A cold-blooded reptile basks on a warm rock in the sun. Its body is warmed
by
a. | radiation. | c. | convection. | b. | conduction. | d. | Both (a) and
(b) |
|
|
|
4.
|
An internal combustion engine uses what kind of energy to do work?
a. | radiation | c. | solar | b. | heat | d. | electrical |
|
|
|
5.
|
Temperature is a measure of the average _____ energy of an object’s
particles.
a. | mechanical | c. | potential | b. | kinetic | d. | light |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which of the following is the name of a temperature scale?
a. | Celsius | c. | Kelvin | b. | Fahrenheit | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
7.
|
Convert 75°C to degrees Fahrenheit.
a. | 74°F | c. | 150°F | b. | 102°F | d. | 167°F |
|
|
|
8.
|
The temperature at which all molecular motion stops is
a. | 0°C. | c. | 0 K. | b. | 0°F. | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
9.
|
Convert 500°F to degrees Celsius.
a. | 260°C | c. | 842°C | b. | 296°C | d. | 958°C |
|
|
|
10.
|
When one feels a warm oven, the sensation of warmth is the result of
a. | energy transfer. | c. | contraction of molecules. | b. | potential
energy. | d. | molecular
transfer. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Convert 300 K to the Celsius scale.
|
|
|
12.
|
Convert 458 K to the equivalent Fahrenheit temperature.
a. | 185°F | c. | 365°F | b. | 237°F | d. | 731°F |
|
|
|
13.
|
The energy transferred between objects with different temperatures is
a. | absolute zero. | c. | potential. | b. | heat. | d. | cold. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following temperatures is impossible to measure?
a. | -85°F | c. | -20 K | b. | -50°C | d. | 545°F |
|
|
|
15.
|
_____ describes how much energy is required to raise an object’s
temperature.
a. | Conduction | c. | Specific heat | b. | Radiation | d. | Convection |
|
|
|
16.
|
Calculate the energy transferred when raising the temperature of 16 kg of water
by 3°C (c = 4,186 J/kg • K).
a. | 785 J | c. | 1.26 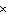 105 J 105 J | b. | 2.2
kJ | d. | 2.0 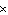 105 J
105 J |
|
|
|
17.
|
_____ does not involve the movement of matter.
a. | Conduction | c. | Heat | b. | Radiation | d. | Convection |
|
|
|
18.
|
Calculate the specific heat for a 20 g piece of metal if 30 J of energy is
required to raise its temperature by 12.5 K.
a. | 0.12 J/kg • K | c. | 120 J/kg • K | b. | 7.5 J/kg • K | d. | 48 kJ/kg •
K |
|
|
|
19.
|
Heat always moves from an object of _____ temperature to an object of _____
temperature.
a. | moderate, high | c. | lower, higher | b. | higher, lower | d. | zero, high |
|
|
|
20.
|
A drill bit will get hot after extended use. This is because of
a. | potential energy. | c. | mechanical heating. | b. | refrigeration. | d. | solar heating. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Solar panels gather _____ energy from the sun.
a. | kinetic | c. | potential | b. | radiated | d. | mechanical |
|
|
|
22.
|
When energy is transformed, the amount of usable energy
a. | decreases. | c. | increases. | b. | remains constant. | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
23.
|
A solar heating system that utilizes an electric fan to move warm air throughout
a home is called a(n) _____ system.
a. | active | c. | convective | b. | aggressive | d. | passive |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which item below contains insulation material?
a. | stainless steel fork | c. | brass nail | b. | aluminum pie pan | d. | plastic foam
cup |
|
|
|
25.
|
Evaporation causes a _____ effect.
a. | basking | c. | cooling | b. | radiation | d. | heating |
|
|
|
26.
|
Heat engines use _____ to convert potential chemical energy and internal kinetic
energy into mechanical energy.
a. | conduction | c. | radiation | b. | combustion | d. | convection |
|
|
|
27.
|
An engine transforms chemical energy of a fuel into work done by
a. | a carburetor. | c. | spark plugs. | b. | friction. | d. | pistons. |
|
|
|
28.
|
The total amount of energy (both usable and unusable) in any process
a. | increases. | c. | remains constant. | b. | decreases. | d. | varies. |
|
|
|
29.
|
What is 37.0 degrees Celsius on the Fahrenheit scale?
a. | 98.6°F | c. | 92.0°F | b. | 87.0°F | d. | 102.0°F |
|
|
|
30.
|
As the kinetic energy of the molecules in a substance increases, the
a. | temperature of the substance increases. | b. | temperature of the
substance decreases. | c. | potential energy of the substance
changes. | d. | temperature remains the same. |
|