Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
____________________a self-replicating material
present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of
genetic information.
a. | RNA | b. | Deoxyribonucleic acid | c. | Deoxyribose | d. | protein
synthesis |
|
|
|
2.
|
____________________A molecule used to translate the
code from the DNA molecule into protein.
a. | RNA | b. | Deoxyribonucleic acid | c. | Deoxyribose | d. | protein
synthesis |
|
|
|
3.
|
____________________ transfer RNA that contains this
three-part nucleotide segment which is an exact complement of one mRNA codon
a. | anticodon | b. | start codon | c. | codon | d. | stop codon |
|
|
|
4.
|
____________________ A three-nucleotide that has the
specific function of corresponding to a particular amino acid.
a. | anticodon | b. | start codon | c. | codon | d. | stop codon |
|
|
|
5.
|
____________________ the first three-nucleotide
segment
a. | anticodon | b. | start codon | c. | codon | d. | stop codon |
|
|
|
6.
|
____________________ - a three~nucleotide segment
that tells the ribosome that the translation process is complete
a. | anticodon | b. | start codon | c. | codon | d. | stop codon |
|
|
|
7.
|
____________________ - pieces of the DNA molecule
that code for specific proteins.
a. | RNA | b. | gene | c. | chromosomes | d. | codon |
|
|
|
8.
|
____________________- a sugar that combines with a
nitrogenous base to form a phosphate group used in nucleotides -building blocks of nucleic
acids.
a. | RNA | b. | Deoxyribonucleic acid | c. | Deoxyribose | d. | protein
synthesis |
|
|
|
9.
|
____________________a process of making genes into
proteins
a. | RNA | b. | Deoxyribonucleic acid | c. | Deoxyribose | d. | protein
synthesis |
|
|
|
10.
|
____________________ - An enzyme that picks up
these unattached DNA.
a. | RNA polymerase | b. | gene | c. | ribose | d. | ribosome |
|
|
|
11.
|
____________________ - complementary base with
cytosine.
a. | Guanine | b. | adenine | c. | cytosine | d. | thymine |
|
|
|
12.
|
____________________ - complementary base with
thymine.
a. | Guanine | b. | adenine | c. | cytosine | d. | thymine |
|
|
|
13.
|
____________________ - complementary base with
uracil in RNA
a. | Guanine | b. | adenine | c. | cytosine | d. | thymine |
|
|
|
14.
|
____________________ - building blocks of nucleic
acids
a. | Nucleotides | b. | codons | c. | enzymes | d. | hormones |
|
|
|
15.
|
____________________ - a polypeptide formed during
translation
a. | Nucleotides | b. | amino acids | c. | enzymes | d. | hormones |
|
|
|
16.
|
____________________ - step in protein synthesis
where mRNA is decoded (translated) and a corresponding polypeptide is formed.
a. | translation | b. | transcription | c. | protein
synthesis | d. | ribosomal RNA |
|
|
|
17.
|
____________________ - copying process that
manufactures of a specific kind of RNA called messenger RNA
a. | translation | b. | transcription | c. | protein
synthesis | d. | ribosomal RNA |
|
|
|
18.
|
____________________ - that help to carry out
reactions within the cell.
a. | amino acid | b. | hormone | c. | protein
synthesis | d. | enzyme |
|
|
|
19.
|
____________________ - chemical messengers that
regulate some body functions
a. | amino acids | b. | hormones | c. | protein
synthesis | d. | enzymes |
|
|
|
20.
|
Protein synthesis begins with the manufacture of which molecule?
a. | mRNA | b. | rRNA | c. | tRNA
| d. | nucleotide |
|
|
|
21.
|
What are ribosomes made of?
a. | mRNA | b. | rRNA | c. | tRNA
| d. | protein |
|
|
|
22.
|
Proteins are made up of polypeptide chains. Polypeptide chains are composed
of
a. | mRNA | b. | rRNA | c. | tRNA
| d. | amino acids |
|
|
|
23.
|
What does transfer RNA (tRNA) carry?
a. | the mRNA to the ribosome | b. | the nucleotide bases to the
mRNA | c. | an amino acid to the ribosome | d. | an amino acid to the
cytoplasm |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following is the first step in protein synthesis?
a. | tRNA bonds to an amino acid in the cytoplasm | b. | DNA unravels to
expose an mRNA | c. | DNA unravels to expose a gene segment. | d. | mRNA bonds to
tRNA.
|
|
|
|
25.
|
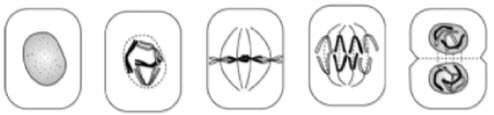 Match the following with the correct sequence of
Transcription. a. | Prophase, Interphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Mitosis | b. | Interphase,
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Mitosis | c. | Interphase, Prophase, Anaphase, Metaphase,
Mitosis | d. | Interphase, Mitosis, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which one is NOT one of three basic steps to manufacture or assemble the
proteins that occur outside the nucleus on the ribosome?
a. | the DNA code of the gene segments must be copied in the nucleus of cell.
| b. | The code must be carried from the nucleus into the cytoplasm and finally to a
ribosome. | c. | The protein has been assembled in the cytoplasm on the surface of the ribosome and
released | d. | identical cells are duplicated |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which one is NOT one of 4 bases of DNA?
a. | Uracil | b. | Thymine | c. | Cytosine | d. | Adenine |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which one is NOT one of 4 bases of RNA?
a. | Uracil | b. | Thymine | c. | Cytosine | d. | Adenine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.
|
Refer to the illustration above. The cell in diagram 1 is in
a. | metaphase. | c. | anaphase. | b. | telophase. | d. | prophase. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Mitosis begins with the stage shown in
diagram
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Which of the following correctly indicates the
order in which these events occur?
a. | A, B, C, D | c. | B, A, C, D | b. | C, B, A, D | d. | A, C, B, D |
|
|
|
32.
|
Refer to the illustration above. During which stage do the centromeres
divide?
|
|
|
33.
|
In eukaryotes, the cell cycle is controlled by
a. | proteins. | c. | lipids. | b. | carbohydrates. | d. | fats. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Molecules of DNA are composed of long chains of
a. | amino acids. | c. | monosaccharides. | b. | fatty acids. | d. | nucleotides. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following is not part of a molecule of DNA?
a. | deoxyribose | c. | phosphate | b. | nitrogen base | d. | ribose |
|
|
|
36.
|
A nucleotide consists of
a. | a sugar, a protein, and adenine. | b. | a sugar, an amino acid, and
starch. | c. | a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. | d. | a starch, a
phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. |
|
|
|
37.
|
The part of the molecule for which DNA is named is the
a. | phosphate group. | c. | nitrogen base. | b. | sugar. | d. | hydrogen bonds. |
|
|
|
38.
|
The amount of guanine in an organism always equals the amount of
a. | protein. | c. | adenine. | b. | thymine. | d. | cytosine. |
|
|
|
39.
|
adenine : thymine ::
a. | protein : DNA | c. | guanine : cytosine | b. | Watson : Crick | d. | guanine :
thymine |
|
|
|
40.
|
Which of the following is not true about DNA replication?
a. | It must occur before a cell can divide. | b. | Two complementary
strands are duplicated. | c. | The double strand unwinds and unzips while it
is being duplicated. | d. | The new DNA molecule has two newly-made
strands. |
|
|
|
41.
|
The attachment of nucleotides to form a complementary strand of DNA during
replication
a. | is accomplished by DNA polymerase. | b. | is accomplished only in the presence of
tRNA. | c. | prevents separation of complementary strands of RNA. | d. | is the
responsibility of the proofreading enzymes. |
|
|
|
42.
|
The enzymes responsible for adding nucleotides to the exposed DNA bases during
replication are
a. | replicases. | c. | helicases. | b. | DNA polymerases. | d. | template
enzymes. |
|
|
|
43.
|
Transcription, which is a stage of gene expression, is the process by which
genetic information encoded in DNA is transferred to a(n)
a. | RNA molecule. | c. | uracil molecule. | b. | DNA molecule. | d. | tRNA molecule. |
|
|
|
44.
|
RNA differs from DNA in that RNA
a. | is double-stranded. | c. | contains the nitrogen base uracil. | b. | contains
deoxyribose. | d. | does not
contain adenine. |
|
|
|
45.
|
Which of the following is not found in RNA?
a. | adenine | c. | thymine | b. | cytosine | d. | uracil |
|
|
|
46.
|
RNA is chemically similar to DNA except that the sugar in RNA has an additional
a. | oxygen atom. | c. | nitrogen base. | b. | phosphate group. | d. | carbon atom. |
|
|
|
47.
|
In RNA molecules, adenine is complementary to
a. | cytosine. | c. | thymine. | b. | guanine. | d. | uracil. |
|
|
|
48.
|
Each of the following is a type of RNA except
a. | carrier RNA. | c. | ribosomal RNA. | b. | messenger RNA. | d. | transfer RNA. |
|
|
|
49.
|
During transcription,
a. | proteins are synthesized. | c. | RNA is
produced. | b. | DNA is replicated. | d. | translation occurs. |
|
|
|
50.
|
During transcription, the genetic information for making a protein is
“rewritten” as a molecule of
a. | messenger RNA. | c. | transfer RNA. | b. | ribosomal RNA. | d. | translation
RNA. |
|
|
|
51.
|
Transcription begins when RNA polymerase
a. | attaches to a ribosome. | b. | unwinds a strand of DNA. | c. | binds to a strand of
RNA. | d. | attaches to the promoter sequence of a gene. |
|
|
|
52.
|
Each nucleotide triplet in mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid is called
a(n)
a. | peptide bond. | c. | anticodon. | b. | codon. | d. | helicase. |
|
|
|
mRNA: CUCAAGUGCUUC
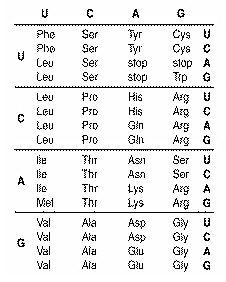
|
|
|
53.
|
Refer to the illustration above. What is the portion of the protein molecule
coded for by a piece of mRNA with the sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC?
a. | Ser—Tyr—Arg—Gly | c. | Leu—Lys—Cys—Phe | b. | Val—Asp—Pro—His | d. | Pro—Glu—Leu—Val |
|
|
|
54.
|
Refer to the illustration above. The anticodons for the codons in the mRNA with
the sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC are
a. | GAG—UUC—ACG—AAG. | c. | CUC—GAA—CGU—CUU. | b. | GAG—TTC—ACG—AAG. | d. | CUU—CGU—GAA—CUC. |
|
|
|
55.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Which of the following would represent the
strand of DNA from which the mRNA strand CUCAAGUGCUUC was made?
a. | CUCAAGUGCUUC | c. | GAGTTCACGAAG | b. | GAGUUCACGAAG | d. | AGACCTGTAGGA |
|
|
|
| mRNA codons | amino acid | | UAU, UAC | tyrosine | | CCU, CCC, CCA, CCG | proline | | GAU, GAC | aspartic acid | | AUU, AUC,
AUA | isoleucine | | UGU, UGC | cysteine | | |
|
|
|
56.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Suppose that you are given a protein containing
the following sequence of amino acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine.
Use the portion of the genetic code given to determine which of the following contains a DNA sequence
that codes for this amino acid sequence.
a. | AUGGGUCUAUAUACG | c. | GCAAACTCGCGCGTA | b. | ATGGGTCTATATACG | d. | ATAGGGCTTTAAACA |
|
|
|
57.
|
The function of rRNA is to
a. | synthesize DNA. | c. | form ribosomes. | b. | synthesize mRNA. | d. | transfer amino acids to
ribosomes. |
|
|
|
58.
|
At the very beginning of translation, the first tRNA molecule
a. | binds to the mRNA’s anticodon. | b. | attaches directly to the DNA
codon. | c. | connects an amino acid to its anticodon. | d. | binds to the
mRNA’s start codon. |
|
|
|
59.
|
Transfer RNA
a. | carries an amino acid to its correct codon. | b. | synthesizes amino
acids as they are needed. | c. | produces codons to match the correct
anticodons. | d. | converts DNA into mRNA. |
|
|
|
60.
|
Which cell organelle contains its own DNA?
a. | the Golgi apparatus | c. | the plasma membrane | b. | the mitochondria | d. | the ER |
|