Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
All organic compounds contain the element
|
|
|
2.
|
Which of the following is a carbohydrate?
a. | DNA | c. | wax | b. | insulin | d. | sucrose |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which organic molecules below are classified as carbohydrates?
a. | amino acids | c. | nucleotides | b. | fatty acids | d. | sugars |
|
|
|
4.
|
Animals store glucose in the form of
a. | cellulose. | c. | wax. | b. | glycogen. | d. | lipids. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Polysaccharides are
a. | carbohydrates. | c. | proteins. | b. | lipids. | d. | unsaturated
fats. |
|
|
|
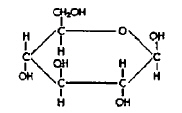 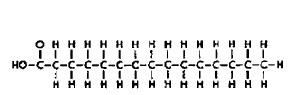 Molecule
A
Molecule B
Molecule
A
Molecule B
|
|
|
6.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Molecules like Molecule B are found in
a. | carbohydrates. | c. | nucleic acids. | b. | lipids. | d. | proteins. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Lipids are
a. | polar molecules. | c. | water soluble. | b. | similar to water molecules. | d. | nonpolar
molecules. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which organic molecules below are most closely related to proteins?
a. | amino acids | c. | nucleotides | b. | fatty acids | d. | sugars |
|
|
|
9.
|
All of the following are examples of lipids except
a. | saturated fats. | c. | cholesterol. | b. | starch. | d. | earwax. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Lipids are soluble in
a. | water. | c. | oil. | b. | salt water. | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which organic molecules below are most closely related to lipids?
a. | amino acids | c. | nucleotides | b. | fatty acids | d. | sugars |
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Which structure immediately identifies this
cell as a eukaryote?
a. | structure 1 | c. | structure 3 | b. | structure 2 | d. | structure 4 |
|
|
|
13.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Structure 1 is
a. | endoplasmic reticulum. | c. | a mitochondrion. | b. | a Golgi apparatus. | d. | the nucleus. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Refer to the illustration above. The cell uses structure 3 to
a. | transport material from one part of the cell to another. | b. | package proteins so
they can be stored by the cell. | c. | use light energy to make
sugar. | d. | use energy from organic compounds to make ATP. |
|
|
|
15.
|
Refer to the illustration above. In eukaryotic cells, DNA is found in
a. | structure 1. | c. | structure 3. | b. | structure 2. | d. | structure 5. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Refer to the illustration above. The cell shown is probably an animal cell
because it
a. | has mitochondria. | c. | has a cell membrane. | b. | does not have a cell wall. | d. | does not have a
nucleus. |
|
|
|
17.
|
The double membrane surrounding the nucleus is called the
a. | nucleolus. | c. | ribosome. | b. | nuclear wall. | d. | nuclear
envelope. |
|
|
|
18.
|
In a cell, proteins are made on the
a. | mitochondria. | c. | nucleus. | b. | ribosomes. | d. | cell membrane. |
|
|
|
19.
|
The organelles associated with plant photosynthesis are the
a. | mitochondria. | c. | Golgi apparatus. | b. | chloroplasts. | d. | vacuoles. |
|
|
|
20.
|
All the following are found in both plant and animal cells, except
a. | a cell wall. | c. | mitochondria. | b. | a cell membrane. | d. | endoplasmic
reticulum. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Amino acids are monomers of
a. | disaccharides. | c. | nucleotides. | b. | proteins. | d. | steroids. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Nucleic acids include
a. | chlorophyll and retinal. | c. | lipids and
sugars. | b. | DNA and RNA. | d. | glucose and glycogen. |
|
|
|
23.
|
The earliest known group of living organisms on Earth was
a. | viruses. | c. | bacteria. | b. | fungi. | d. | protists. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Bacteria are the only organisms characterized as
a. | unicellular. | c. | eukaryotic. | b. | prokaryotic. | d. | photosynthetic. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Bacteria can be classified according to their
a. | type of cell walls. | c. | Gram-staining characteristics. | b. | methods of obtaining
energy. | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Which of the diagrams has a shape like the
Bacillus bacterial genus?
a. | Organism “A” | c. | Organism
“C” | b. | Organism “B” | d. | None of the above |
|
|
|
27.
|
Refer to the illustration above. The shape represented by Organism
“C” is called
a. | coccus. | c. | bacillus. | b. | spirillum. | d. | filamentous. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Bacteria lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles; therefore, they are
classified as
a. | prokaryotes. | c. | anaerobes. | b. | aerobes. | d. | eukaryotes. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the following might be found in the cytoplasm of a bacterial
cell?
a. | chloroplasts | c. | mitochondria | b. | Golgi bodies | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following are used by at least some bacteria for movement?
a. | pili | c. | cytoplasmic projections | b. | flagella | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
31.
|
A pathogen is an agent that is
a. | beneficial to humans. | c. | harmful to living organisms. | b. | harmful only to
plants. | d. | nearly
extinct. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Antibiotics
a. | include penicillin, tetracycline, and streptomycin. | b. | may prevent bacteria
from making new cell walls. | c. | are very effective treatments for bacterial
diseases. | d. | All of the above |
|
|
|
33.
|
Hooke’s discovery of cells was made observing
a. | living algal cells. | c. | dead plant cells. | b. | living human blood cells. | d. | dead protist
cells. |
|
|
|
34.
|
The smallest units of life in all living things are
a. | cells. | c. | cytoplasm. | b. | mitochondria. | d. | Golgi
apparatus. |
|
|
|
35.
|
A cell that can change its shape would be well suited for
a. | receiving and transmitting nerve impulses. | b. | covering the body
surface. | c. | moving to different tissues through narrow openings. | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
36.
|
One difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that
a. | nucleic acids are found only in prokaryotes. | b. | mitochondria are
found in larger quantities in eukaryotes. | c. | Golgi vesicles are found only in
prokaryotes. | d. | prokaryotes have no nuclear membrane. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following is characteristic of prokaryotes?
a. | They have a nucleus. | b. | They were found on Earth before
eukaryotes. | c. | The organelles in their cytoplasm are surrounded by membranes. | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which of the following is an example of a prokaryotic cell?
a. | amoeba | c. | bacterium | b. | virus | d. | liver cell |
|
|
|
39.
|
Only eukaryotic cells have
a. | DNA. | c. | ribosomes. | b. | membrane-bound organelles. | d. | cytoplasm. |
|
|
|
40.
|
Studying a picture of a cell taken with an electron microscope, you find that
the cell has no nucleus and no mitochondria, but it does have a cell membrane and a cell wall. You
conclude that the cell is probably from a(n)
a. | animal. | c. | prokaryote. | b. | plant. | d. | now extinct
organism. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Cell membranes
a. | are only found on a small number of cells. | b. | contain
genes. | c. | are made of DNA. | d. | are thin coverings that surround
cells. |
|
|
|
42.
|
The structure that regulates what enters and leaves the cell is called
a. | the nucleus. | c. | the nuclear membrane. | b. | the cell
wall. | d. | the cell
membrane. |
|
|
|
43.
|
The cell membrane
a. | encloses the contents of a cell. | b. | allows material to enter and leave the
cell. | c. | is selectively permeable. | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
44.
|
A structure within a cell that performs a specific function is called
a(n)
a. | organelle. | c. | tissue. | b. | organ tissue. | d. | biocenter. |
|
|
|
45.
|
A particularly active cell might contain large numbers of
a. | chromosomes. | c. | mitochondria. | b. | vacuoles. | d. | walls. |
|
|
|
46.
|
Golgi apparatus are organelles that
a. | receive proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum. | b. | label the molecules
made in the endoplasmic reticulum with tags that specify their destination. | c. | release molecules in
vesicles. | d. | All of the above |
|
|
|
47.
|
In which of the following organelles is a cell’s ATP produced?
a. | mitochondrion | c. | Golgi apparatus | b. | endoplasmic reticulum | d. | lysosome |
|
|
|
48.
|
Numerous threadlike organelles that protrude from the surface of a cell and are
packed in tight rows are called
a. | flagella. | c. | actin filaments. | b. | microtubules. | d. | cilia. |
|
|
|
49.
|
The packaging and distribution center of the cell is the
a. | nucleus. | c. | central vacuole. | b. | Golgi apparatus. | d. | nuclear
envelope. |
|
|
|
50.
|
All cells have
a. | a covering called a membrane that surrounds the cell and controls what information
and materials enter and leave it. | b. | an internal fluid that gives shape to the cell
and supports the other things within it. | c. | a central zone or nucleus that contains the
cell's genes. | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
51.
|
How are chloroplasts like mitochondria?
a. | They can both use energy from sunlight. | b. | They look
alike. | c. | They both manufacture food and release energy. | d. | They are both found
in animal cells. |
|
|
|
52.
|
The organelles in plant cells that contain a green pigment are the
a. | mitochondria. | c. | chloroplasts. | b. | bilayer lipids. | d. | Golgi
apparatus. |
|
|
|
53.
|
Plant cells have large membrane-bound spaces in which water, waste products, and
nutrients are stored. These places are known as
a. | mitochondria. | c. | Golgi apparatus. | b. | chloroplasts. | d. | vacuoles. |
|
|
|
54.
|
A model of enzyme action is the
a. | induced fit model | c. | activator action model | b. | lipid bilayer
model | d. | acive site
model |
|
|
|
55.
|
All of the following are functional groups
except
a. | a hydroxyl group. | c. | a carboxyl group | b. | a amino group | d. | a carbonate
group |
|
|
|
56.
|
Which of the following is the correct order of organization of structures in
living things, from simplest to most complex?
a. | organ systems, organs, tissues, cells | b. | tissues, cells, organs, organ
systems | c. | cells, tissues, organ systems, organs | d. | cells, tissues, organs, organ
systems |
|
|
|
57.
|
Without enzymes, the chemical reactions in the body
would
a. | happen too fast | b. | occur at much the same rate as they do with
enzymes. | c. | require a different pH. | d. | occur too slowly to support life
processes |
|
|
|
58.
|
Carbon atoms can bond together to form all of the following
except
a. | ring structures | b. | inorganic structures | c. | straight chain
structures. | d. | branched structures |
|
|
|
59.
|
Prokaryotes can transfer pieces of genetic material
in a process called
a. | binary fission | b. | mitosis | c. | conjugation | d. | sexual
reproduction |
|
|
|
60.
|
Which of the following is not a way of
preventing a foodborne illness at home?
a. | washing kitchen utensils thoroughly in cold water | b. | keeping cooked and
raw foods separate during storage | c. | washing fresh fruits and vegetables before
eating them | d. | refrigerating leftovers
promptly |
|